One of the very great strengths of Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is discerning what is going on inside the body from watching, smelling, asking, and touching the patients. With more than 2000 years of curing culture, Chinese medicine practitioners have correlated the external and internal human body with disease patterns or tendencies to manifest particular disease patterns. But it was only the recent years that TCM practitioners incorporated into their diagnostic techniques two more external signs – the measurement of basal body temperature and the production of cervix mucus just before ovulation. These two observations are essentials for the treatment of infertility, or from another angle, increase the chance of conception.
Basal Body Temperature (BBT)
Basal Body Temperature is the lowest body temperature, measured immediately after waking and before getting out of bed when the metabolism is at its baseline. BBT rises after ovulation, so it can be used as an indicator of natural family planning.
Measuring BBT
Both mercury and digital thermometer can be used to measure basal body temperature. Digital basal thermometers are more common nowadays, as they are safer and are a little easier to read, especially in those groggy first few minutes of the day just after waking. Oral basal thermometers are normally used, although BBT can also be measured by placing the thermometer in the vagina or rectum.
Charting BBT
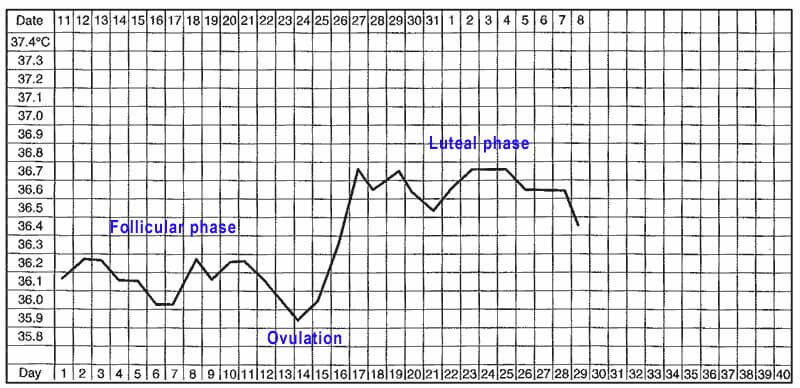
By measuring BBT every day, you will see the pattern of your basal body temperature. Other than ovulation, TCM practitioners can use the BBT chart to understand more about the balance of your body. It is essential that the temperature is read at roughly the same time each morning, as later waking raises the basal body temperature. Studies have shown that BBT rises 0.09ºC for each hour of delayed rising in the morning. In a typical menstrual cycle, a BBT chart looks something like this.
- Follicular phase – the first half of the cycle before ovulation should record relatively lower temperatures.
- Luteal phase – after ovulation the temperatures should remain at a relatively higher level for 12-14 days
- Ovulation – the day before the temperatures become elevated is the most likely day of ovulation
Diagnosis from the BBT chart
The follicular phase could be low, long, short, high, high initially, and unstable. The luteal phase could be short, slightly short, low, unstable sawtooth, unstable saddle, slow-rise, early decline, and long. After reading the basal body temperature charts, the Chinese Medicine practitioners will have a much better idea of the cause and cure of infertility. For examples
- If the follicular phase is consistently short, say only 9 or 10 days, then the TCM practitioner will use treatments to attempt to lengthen it. The short follicular phase could be due to the fact that egg is released only a few days after the end of a period, chances are it will not be as fully developed as possible. In this case, both herbs and acupuncture can be used.
- If the luteal phase is too low, say only 0.1 or 0.2ºC (stead of normal 0.4 – 0.5ºC) above the follicular phase, it represents the imbalance of kidney Yin and Yang. Herbal formulas will be recommended.
Cervical Mucus
Cervical mucus is a type of vaginal discharge. The importance of recognizing the changes in the mucus lies in the fact that it precedes ovulation and therefore alerts a woman to her most fertile days.
Characteristics
After a menstruation cycle, the cervical discharge is thick, pasty, and impenetrable, which results in dry feeling at the vulva. When an ovum (egg) starts to ripen, the mucus will become sticky or wet. As ovulation approaches, mucus will turn into more stretchy and slippery. The amount of this egg-white-like mucus reaches the peak during ovulation, and the sensation at the vulva now is distinctly wet. The phenomenon which gives this mucus its elasticity is called spinnbarkeit, or spin for short.
Functions
- Cervical mucus provides a healthy environment for sperm. With cervical mucus, sperm can steadily swim upwards to the uterus over a period of 2~3 days. Thus, cervical mucus can act as a sperm reservoir.
- Cervical mucus provides a rapid sperm transit system, as it creates clear pathways for the sperm to swim upwards to the uterus.
- Cervical mucus can block and filter out some of the abnormal or poor-quality sperm before they reach the uterus.
TCM and Cervical Mucus
If the cervical mucus is inadequate in quality or quantity, there are Chinese herbal treatments which can be used to address this. Treatment of cervical mucus is especially essential for infertility if sperm numbers or motility are low.
The advantage of combing the BBT measurements with the observations of the cervix and its secretions is that they provide complementary information and corroborate each other. Only the fertile mucus can indicate that ovulation is about to happen, but only the temperature shift observed in the BBT can show that ovulation has happened.

